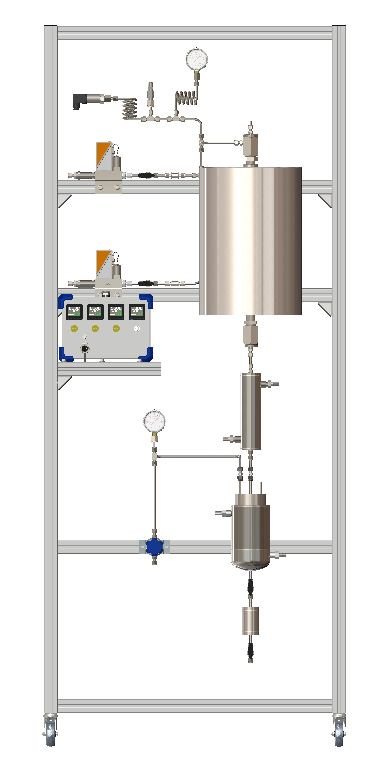
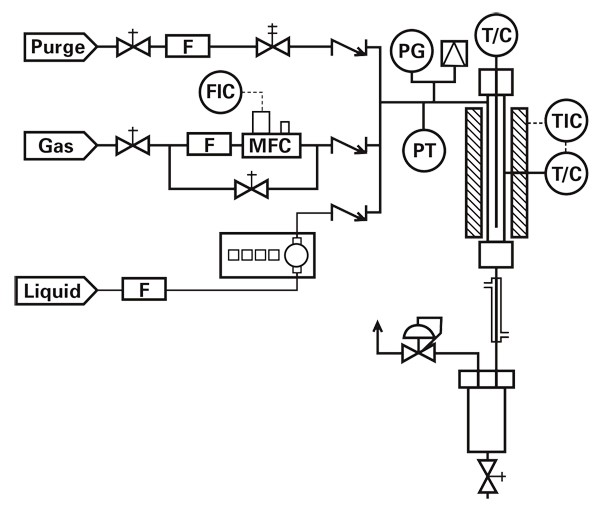
CONTINUOUS FLOW TUBULAR REACTOR
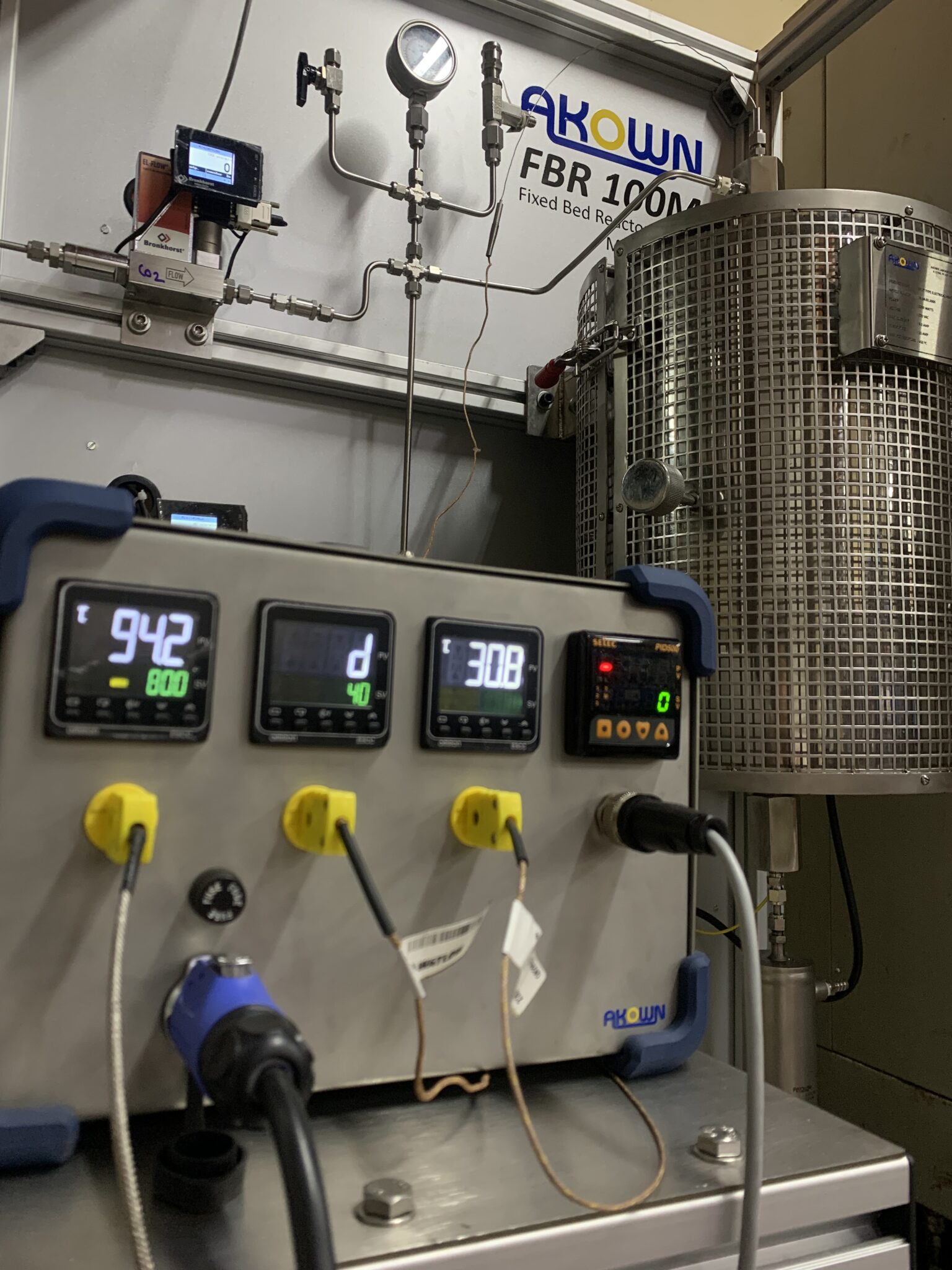

Tubular reactors are used in continuous flow mode with reagents flowing in and products flowing out. They can be the simplest of all reactor designs. Tubular reactors are often referred to by a variety of names:
- Plug flow reactors
- Pipe reactors
- Packed-bed reactors
- Fixed-bed reactors
- Trickle-bed reactors
- Bubble-column reactors
- Ebullating-bed reactors
Single-phase flow in a tubular reactor can be upward or downward. Two-phase flow can be co-current up-flow, counter-current (liquid down, gas up) or, most commonly, co-current down-flow
Tubular reactors are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Carbonylation
- Dehydrogenation
- Hydrogenation
- Hydrocracking
- Hydroformulation
- Oxidative decomposition
- Partial oxidation
- Polymerization
- Reforming
- Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis
- Ammonia Synthesis
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Reactor Type | Tubular Continuous Flow |
| Material of Construction | SS316 / SS316L / Hastelloy / Inconel / Titanium |
| Operating Pressure | Up to 100 bar (customizable up to 350 bar) |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 400°C (optional up to 800°C with special materials) |
| Tubing Inner Diameter | 1 inch to 4 inch (customizable) |
| Flow Rate Range | Based on pump configuration |
| Heating Method | Electric Heating Jacket |
| Pressure Control | Back Pressure Regulator (manual or automated) |
| Temperature Control | PID-based controller with thermocouple / RTD sensors |
| Pump Type | HPLC / Syringe / Gear / Diaphragm (based on flow & pressure needs) |
| Safety Features | Pressure relief valve, over-temperature cutoff, rupture disc (optional) |
| Mounting | Skid-mounted / Bench-top Modular Unit |
| Additional Features | Real-time data logging, integration with SCADA or LabVIEW (optional) |